Introduction
What’s the real cost behind building powerful logistics software? In today’s fast-paced world, efficient logistics management can make or break a business. From real-time tracking to route optimization, logistics software must be robust, scalable, and tailored to complex supply chain needs. However, many businesses underestimate the investment required to develop such a sophisticated system.
Building powerful logistics software involves multiple components — a user-friendly interface, seamless integration with GPS and IoT devices, data analytics capabilities, and secure cloud infrastructure. Each feature demands expert development, rigorous testing, and ongoing maintenance. Moreover, incorporating AI and machine learning to optimize routes or predict delivery times adds to the complexity and cost.
Choosing the right software development partner is crucial to balance quality and budget. True Value Infosoft, recognized as the best software development company in India, excels in delivering custom logistics solutions that combine innovation, reliability, and affordability. Their experienced team understands the unique challenges of the logistics industry and crafts scalable software tailored to your business goals. With True Value Infosoft, you gain a partner who not only develops top-notch logistics software but also ensures cost-effective strategies throughout the development lifecycle, making your investment worthwhile.
Understanding Logistics Software: What Are We Building?
Before diving into costs, it’s crucial to understand what logistics software entails. Logistics software manages the flow of goods, information, and resources from point A to point B, optimizing routes, tracking shipments, managing warehouse operations, and handling inventory, among other tasks. Common types include:
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Focused on planning, executing, and optimizing the physical movement of goods.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Streamlines warehouse operations such as inventory tracking, picking, and packing.
- Fleet Management Software: Manages vehicles, drivers, maintenance schedules, and compliance.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software: Coordinates supply chain activities from raw material procurement to product delivery.
Each of these modules can be standalone or integrated to form an all-encompassing logistics platform.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Logistics Software Development

Building logistics software is not a one-size-fits-all project. Costs fluctuate widely depending on several key factors:
1. Scope and Features
The scope directly impacts development time and cost. Basic software with essential features like shipment tracking and order management will cost significantly less than a comprehensive solution with advanced functionalities such as AI-powered route optimization, real-time fleet tracking, predictive analytics, and automated warehouse management.
Key features influencing cost include:
- Real-time GPS tracking
- Route planning and optimization
- Inventory management
- Automated alerts and notifications
- Integration with third-party carriers and ERP systems
- Billing and invoicing
- Customer portals and dashboards
- Reporting and analytics
The more complex and feature-rich your logistics software, the higher the development cost.
2. Platform and Technology Stack
The choice of platform—whether web, mobile (iOS, Android), or desktop—and technology stack influences both initial development and long-term maintenance costs.
- Web-based platforms: Accessible via browsers, allowing wide usage but may require robust backend servers.
- Mobile apps: Necessary for drivers, warehouse staff, or customers needing real-time updates.
- Hybrid or Native Mobile Apps: Native apps tend to be costlier but offer better performance.
Technology choices such as React, Angular, Node.js, Python, Java, or cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud also impact costs depending on developer availability, licensing fees, and infrastructure expenses.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Logistics software often needs to integrate with:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools
- Payment gateways
- Third-party carrier APIs
- IoT devices (for real-time tracking)
Each integration requires time and expertise, adding to development costs.
4. User Roles and Permissions
Logistics software typically involves multiple user roles, each requiring different access levels and interfaces:
- Admins or managers
- Drivers and field personnel
- Warehouse operators
- Customers or suppliers
Customizing features and interfaces for each role increases design and development complexity.
5. Geographical Coverage and Compliance
If the software must operate across multiple countries or regions, it must handle different currencies, languages, tax laws, and regulatory compliance. Localization adds layers of complexity and cost.
6. Scalability and Performance
Building software that can scale to accommodate growing shipments, users, and data volumes requires scalable architecture, often involving cloud infrastructure and microservices. This can increase upfront costs but save money long-term by avoiding system rewrites.
7. Security
Given the sensitivity of logistics data—including shipment details, customer information, and payment data—security is paramount. Incorporating data encryption, secure authentication, GDPR compliance, and audit trails adds to development efforts.
8. Design and User Experience
A user-friendly interface for all stakeholders ensures better adoption and efficiency. Investing in UX/UI design, usability testing, and continuous refinement adds to the cost but delivers better ROI.
Development Phases and Their Cost Implications
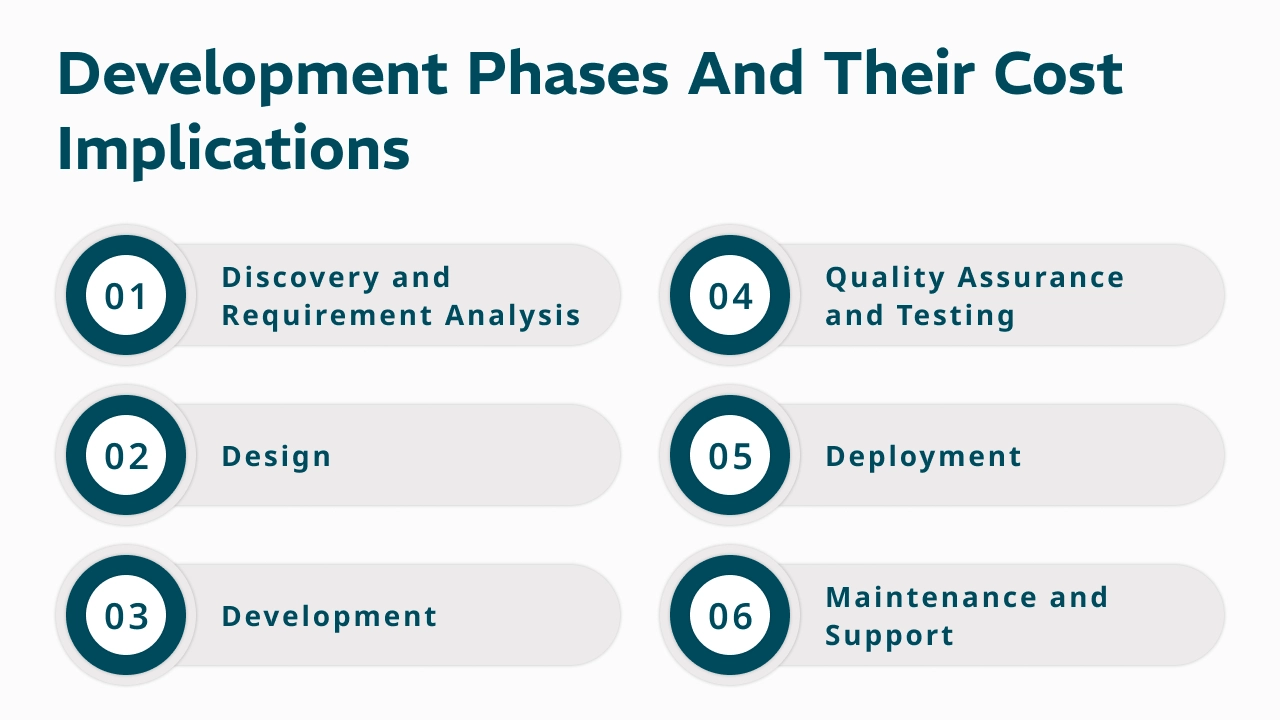
Understanding the software development lifecycle helps break down where your investment goes.
1. Discovery and Requirement Analysis
This initial phase involves identifying business goals, user needs, and technical requirements. It requires workshops, stakeholder interviews, and competitor analysis.
- Cost impact: 5-10% of total project cost
- Duration: 2-4 weeks
A thorough discovery phase prevents costly scope changes later.
2. Design
UI/UX designers create wireframes, mockups, and prototypes.
- Cost impact: 10-15%
- Duration: 3-6 weeks
Good design improves usability and reduces training costs.
3. Development
The largest cost segment, where frontend and backend developers build the software.
- Cost impact: 50-60%
- Duration: 3-9 months, depending on complexity
Includes coding, integration, and unit testing.
4. Quality Assurance and Testing
Involves manual and automated testing for bugs, performance, and security.
- Cost impact: 10-15%
- Duration: Parallel or post-development
Ensures reliability and reduces future maintenance expenses.
5. Deployment
Launching the software, setting up servers, and configuring environments.
- Cost impact: 5%
- Duration: 1-2 weeks
Includes initial training for users.
6. Maintenance and Support
Ongoing updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
- Cost impact: 15-20% annually of initial development cost
Essential for adapting to new business needs and technology upgrades.
Estimated Cost Breakdown by Region
Development costs vary significantly depending on the geographical location of your software development team:
| Region | Hourly Rate (USD) | Estimated Cost for a Mid-size Project (6 months) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | $100 - $250 | $200,000 - $500,000 |
| Western Europe | $80 - $200 | $160,000 - $400,000 |
| Eastern Europe | $30 - $70 | $60,000 - $140,000 |
| India | $15 - $50 | $30,000 - $100,000 |
Choosing offshore or nearshore developers can reduce costs but requires effective communication and project management.
Hidden Costs in Building Logistics Software
Beyond development, some hidden or underestimated costs include:
1. Infrastructure Costs
Cloud hosting, CDN, database licenses, and API usage fees add recurring expenses.
2. Compliance and Legal
Ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance may require legal consultation.
3. Change Management and Training
Introducing new software often demands training staff, adapting processes, and change management, which can be costly and time-consuming.
4. Third-Party Licensing
Using third-party software components or APIs may involve licensing fees or subscription costs.
5. Downtime and Risk Management
Contingency planning for system failures or cybersecurity threats is often overlooked but essential.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies to Optimize Costs
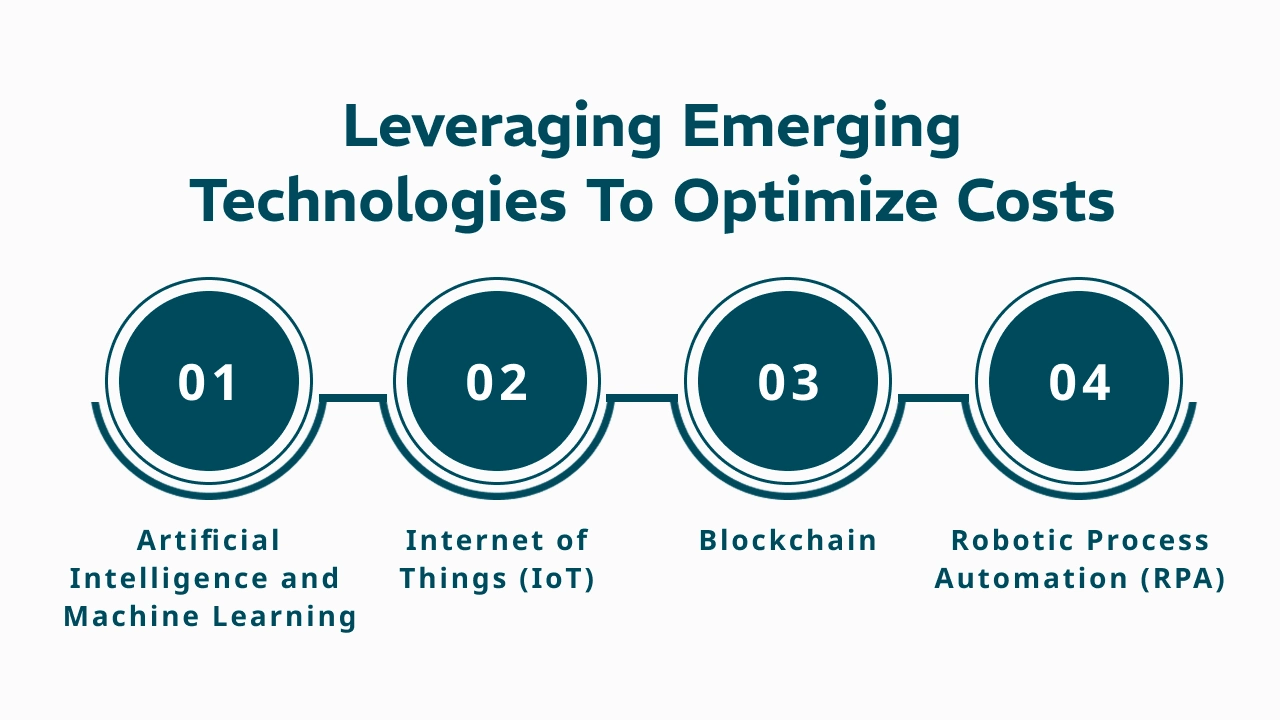
Innovations can optimize costs and enhance logistics software capabilities:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI can automate route planning, demand forecasting, and anomaly detection, reducing manual effort and errors.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices provide real-time data from vehicles, warehouses, and shipments, improving visibility and decision-making.
3. Blockchain
Enhances transparency and traceability in the supply chain, reducing fraud and disputes.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Automates repetitive tasks such as data entry, freeing staff for higher-value work.
Building vs Buying Logistics Software: Cost Considerations
Businesses often face the dilemma of building custom logistics software or buying off-the-shelf solutions.
Buying Off-the-Shelf
- Faster deployment
- Lower upfront cost
- Limited customization
- Subscription or licensing fees
Building Custom Software
- Tailored to exact business processes
- Greater flexibility and scalability
- Higher upfront investment
- Requires in-house or outsourced development expertise
Choosing depends on business size, complexity, and long-term vision.
Cost Optimization Strategies
To keep costs manageable without sacrificing quality, consider:
- MVP Approach: Start with a Minimum Viable Product focusing on core features, then iteratively enhance.
- Agile Development: Enables flexibility and reduces rework.
- Outsourcing: Partnering with reputable offshore developers can save costs.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Pay-as-you-go models reduce upfront hardware investment.
- Open Source Tools: Leverage existing frameworks and libraries to reduce development time.
True Value Infosoft’s Role in Cost-Effective Logistics Software Development
True Value Infosoft Pvt. Ltd. is a leading IT company with extensive experience in developing custom logistics solutions tailored to client needs. Their approach balances cost efficiency with high-quality deliverables by:
- Thoroughly analyzing client requirements to avoid scope creep.
- Utilizing Agile methodologies to ensure iterative development and continuous feedback.
- Offering end-to-end services from design to deployment and maintenance.
- Providing scalable, secure, and future-ready logistics platforms.
- Assisting with integration, compliance, and change management.
This makes True Value Infosoft, Mobile app development company in India seeking powerful yet cost-effective logistics software.
Conclusion
The real cost behind building powerful logistics software extends beyond mere development expenses. It involves careful planning, strategic technology choices, integration challenges, security measures, and ongoing maintenance. By understanding these cost components and leveraging modern development practices, businesses can build logistics software that delivers value, scalability, and competitive advantage.
Partnering with experienced providers like True Value Infosoft ensures not only cost-effectiveness but also access to industry expertise, cutting-edge technologies, and robust support — all crucial to navigating the complexities of logistics software development in today’s dynamic market.
FAQs
Development timelines vary with complexity but typically range from 3 to 9 months for a mid-sized project.
Common technologies include React, Angular, Node.js, Java, Python, cloud platforms like AWS or Azure, GPS APIs, IoT integrations, and AI/ML frameworks.
Generally, custom software has higher upfront costs but offers better alignment with business processes and long-term savings due to flexibility and scalability.
AI enhances route optimization, demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, and anomaly detection, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Ongoing costs include software maintenance, server hosting, security updates, user training, and feature enhancements.